Image Formation by Convex Lens
Image Formation by Convex Lens: Overview
In this topic, we will discuss the characteristics of an image formed by a convex lens with the help of ray diagrams. A lot of examples and illustrations are given for easy understanding of the concepts.
Important Questions on Image Formation by Convex Lens
Draw ray diagrams to show the formation of a three times magnified () real image () virtual image of an object kept in front of a converging lens, mark the positions of object, and position of image clearly in the diagram.
A convex lens has a focal length of . At what distance from the lens should the object be placed so that it forms a real and inverted image away from the lens? What would be the size of the image formed if the object is high? With the help of a ray diagram show the formation of the image by the lens in this case.
Where should an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size is obtained, using a convex lens:
The image formed by a convex lens can be__
Position of the object when convex lens forms a virtual and erect image is
Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary__
If an object is placed between focus and optical centre of convex lens, image formed is__
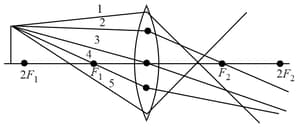
Out of the five incident rays shown in the figure, the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used for locating the position of image formed by a convex lens is _____.
By using a convex lens, a student obtained a sharp image of his class-room window grill on a screen. In which direction should he move the lens to focus a distant tree instead of the grill?
To determine the focal length of a convex lens by obtaining a sharp image of a distant object, the following steps were suggested which are not in proper sequence —
Hold the lens between the object and the screen.
Adjust the position of the lens to form a sharp image.
Select a suitable distant object.
Measure the distance between the lens and the screen.
The correct sequence of steps to determine the focal length of the lens is
Mohan, Sohan and Rahul separately measured the focal length of the same convex lens using the same distant tree as object. All of them measured the distance between the lens and the inverted image of the tree on the screen. Mohan obtained a sharp image on the screen and labelled the measured distance as
Sohan obtained a slightly smaller and somewhat blurred image on the screen. He labelled the measured distance as
Rahul obtained a slightly magnified and blurred image on the screen. He labelled the measured distance as .
The three measured values of focal length are likely to be related as—
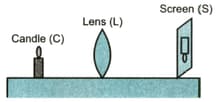
A student performs an experiment on finding the focal length of a convex lens by keeping a lighted candle on one end of laboratory table, a screen on its other end and the lens between them as shown in figure.
The positions of the three are adjusted to get a sharp image of the candle flame on the screen.
If now the candle flame were to be replaced by a distant lamp on a far away electric pole, the student would be able to get a sharp image of this distant lamp on the screen by moving—
A student obtains a blurred image of an object on a screen by using a convex lens. In order to obtain a sharp image of the same object on the screen, he will have to shift the lens:
A student has to determine the focal length of a convex lens by obtaining the image of a distant object on a screen. Which of the following measures should he take to obtain better results?
a) Select a lens of small diameter (say ).
b) Select a lens of larger diameter (say ).
c) Select an object very far from the lens.
d) Select an object far, but not very far, from the lens.
e) Keep all the lights of the room on.
f) Keep minimum lights of the room on.
Given below are a few steps (not in proper sequence) followed in the determination of focal length of a given convex lens by obtaining a sharp image of a distant object—
Measure the distance between the lens and screen.
Adjust the position of the lens to form a sharp image.
Select a suitable distant object.
Hold the lens between the object and the screen with its faces parallel to the screen.
The correct sequence of steps for determination of focal length is—
In an experiment to determine the focal length of a convex lens, a student obtained a sharp, inverted image of a distant tree on the screen behind the lens, she then removed the screen and looked through the lens in the direction of the object. She will see—
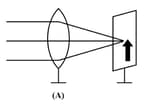
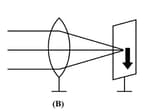
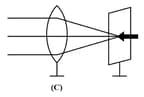
Parallel rays from a distant object incident on a convex lens forms an image on the screen. The diagram showing correctly the image of the object on the screen in figure is—
A teacher gives a convex lens and a concave mirror of focal length of about each to his student and asks him to find their focal lengths by obtaining the image of a distant object. The student uses a distant tree as the object and obtains its sharp image, one by one, on a screen. The distance and between the mirror and the screen in the two cases and the nature of their respective sharp images are likely to be—
To determine the focal length of a convex lens by obtaining a sharp image of a distant object we generally follow the following steps which are not in proper sequence
Hold the lens between the object and the screen.
Measure the distance between the lens and the screen.
Select a well lit distant object.
Place a screen opposite to the object on the lab table.
Adjust the position of the lens to form a sharp image.
The correct sequence of these steps is